Vitamins, including Vitamin C, are organic compounds which exist in living things and are made up of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen. Vitamin C is water-soluble, and our body does not store it and relies solely on dietary intake for maintaining adequate levels.
Unfortunately, Vitamin C deficiency is highly prevalent across India. In a recent study conducted across Indian elders (60 years+), 73.9% of North Indians and 45.7% South Indians were found deficient of Vitamin C [1]. This is alarming as Vitamin C is one of the most vital nutrients and plays an important role in numerous bodily functions.
Functions of Vitamin C
1. Boosts Immunity
Vitamin C is a strong antioxidant that can strengthen the body’s defense against diseases. Antioxidants protect human cells from harmful molecules called free radicals. Accumulation of these free radicals causes oxidative stress which is linked to several chronic diseases. Vitamin C also enhances the regeneration of lymphocytes (white blood cells) which help protect the body against infections. Studies have found that low Vitamin C levels in the body increase the risk of infections.
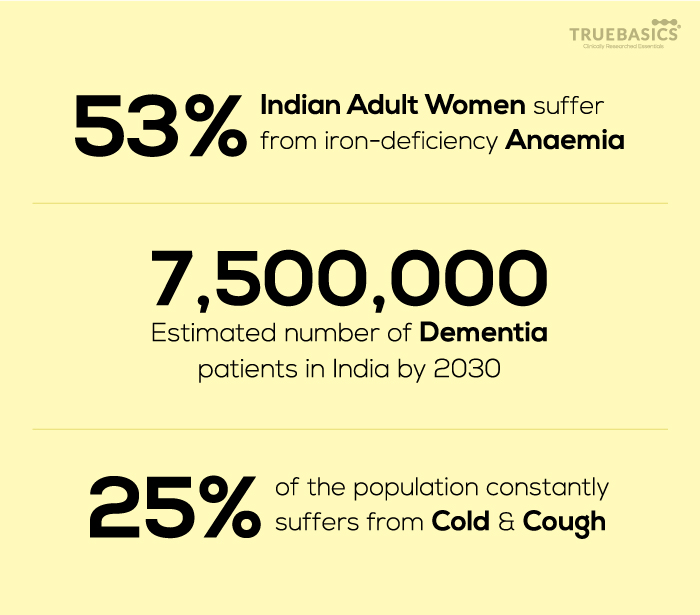
Did you know: In India, around 25% of the population constantly suffers from cold, cough and sore throat [2].
2. Promotes Absorption of Iron
Iron is an important mineral which is essential for the synthesis of red blood cells and oxygen transportation throughout the body. Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) captures non-heme iron and stores it in the body after converting it to a more easily absorbable ferrous ion form. This is especially useful for vegetarians as plant source iron is not bioavailable i.e. our body cannot absorb and utilize it. Vitamin C boosts iron absorption and helps reduce the risk of anemia.
Did you know: 53% of Indian adult women and 23% of Indian adult men suffer from anemia that occurs due to iron deficiency [3].
3. Helps Maintain Skin Elasticity
Collagen provides strength and elasticity to the skin. Vitamin C promotes collagen synthesis and acts as a co-factor for the enzymes proline and lysine hydroxylases that give stability to the collagen structure. A co-enzyme is a non-protein compound that is essential for the functioning of the enzyme. In the absence of Vitamin C, enzymes proline and lysine hydroxylases will be unable to stabilize the collagen structure. Thus, Vitamin C helps in maintaining the structure and elasticity of the skin.
Did you know: 27.9% Indian men and 36.7% Indian women have reported sensitive skin. People with sensitive skin are 3x more likely to suffer from dermatosis [4].
4. Prevents Age-related Memory and Cognitive Function Decline
Ageing causes a decline in
the body’s ability to think and memorize. This is commonly known as dementia.
Researchers have found that inflammation and oxidative stress due to free
radical damage near the central nervous system – brain, spine, and nerves, increases
the risk of dementia. The strong antioxidant action of Vitamin C helps prevent
free radical damage and protects memory and cognition. Low levels of Vitamin C
have been linked to impaired cognitive function while a high intake of Vitamin
C from food or supplements have shown a positive protective effect on memory
and thinking.
Did you know: India would have an estimated 7.5 million dementia and Alzheimer’s patients by 2030 [5].
Since our body is unable to synthesize Vitamin C, adequate intake of Vitamin C rich foods like citrus fruits and vegetables is essential. With today’s fast paced life and processed food products, maintaining an adequate intake of Vitamin C becomes difficult.
5 signs and symptoms you should look out for Vitamin C deficiency
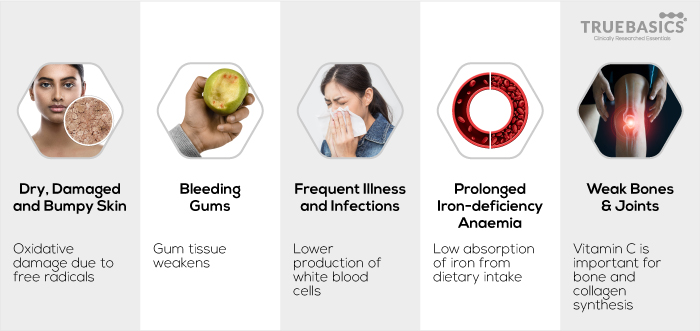
1. Dry, Damaged and Bumpy Skin
With a low intake of Vitamin C, our skin is susceptible to oxidative damage. Also, there is a decline in the synthesis of collagen. The outer layer of skin, called the epidermis, starts to deteriorate. This also causes easy bruising due to thinning of the epidermis and rupturing of blood vessels under the skin. These are the obvious first signs and symptoms of Vitamin C deficiency. Prolonged deficiency can also cause slower wound healing and reopening of wounds.
2. Bleeding Gums
Inflammation and weakening of gums are one of the most common signs of Vitamin C deficiency. The blood vessels in gums bleed more easily and frequently due to weakened tissue. This also leads to calcification of the inner layer of teeth and eventually the teeth can fall due to weak gum tissue holding it in place.
3. Frequent Illness and Infections
Deficiency of Vitamin C leads to lower production of lymphocytes (white blood cells) which are responsible for the body’s innate immunity. A lower number of lymphocytes means that the body is unable to kill invading disease causing pathogens effectively. This increases the risk of infections and frequent illness. A Compromised immune system may lead to further bodily complications which could also become chronic.
4. Prolonged Iron Deficiency Anemia
Low levels or absence of Vitamin C in the body causes iron from dietary intake to go unused. The body requires Vitamin C to convert iron to a more absorbable and usable ferrous ion form. Since the body is unable to absorb iron, it causes anemia. Signs of iron deficiency anemia include fatigue, paleness, difficulty in breathing during exercise, headache, unhealthy skin, hair, and nails. It is advisable to check your Vitamin C levels if iron deficiency persists for a long time.
5. Weak Bones
Vitamin C plays an important role in bone formation. The deficiency of Vitamin C can increase the rate of bone loss. A low level of Vitamin C has also been linked to increased risk of osteoporosis and frequent fractures. Children are especially at a higher risk as their skeletons are growing and developing.
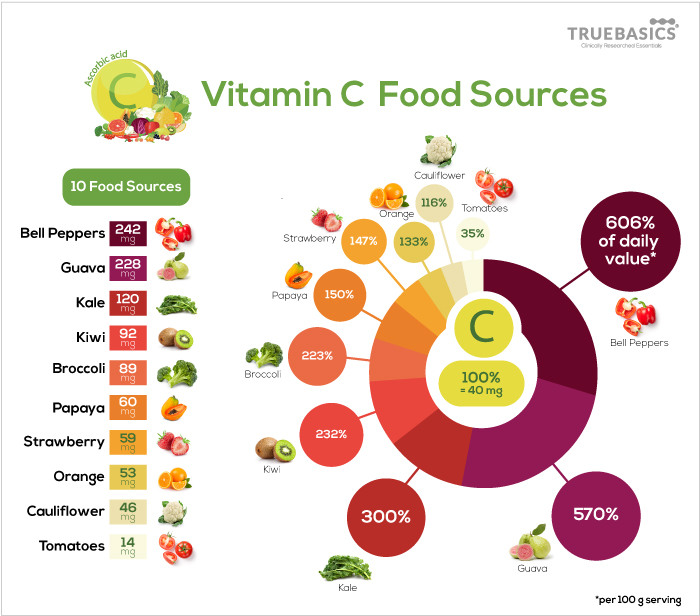
Foods with High Vitamin C content
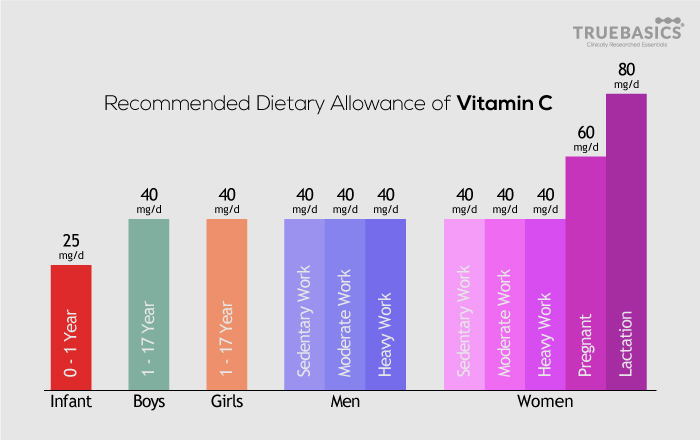
The recommended daily intake of Vitamin C as per the Indian Council of Medical Research is 40 mg per day for both men and women.
Below are the common 6 dietary sources of Vitamin C:
1. Citrus fruits
Citrus fruits are the most common source of Vitamin C with oranges being the most popular one. 100 g of orange contains about 53.2 mg of Vitamin C. Other citrus fruits rich in Vitamin C are Sweet lemons (mosambi) with 53 mg of Vitamin C per 100 g and Lime (nimbu) with 29.1 mg of Vitamin C per 100 g.
2. Bell Peppers
Yellow, red and green bell peppers are a powerhouse of Vitamin C with 242.5 mg per 100 g. Adding bell peppers to your salad will make sure to kick in enough Vitamin C daily.
3. Broccoli
Unknown to many, broccoli has more Vitamin C than an orange with about 89.2 mg per 100 g serving. It is best to consume broccoli with a salad to ensure you retain most of the nutritional value.
4. Papaya
Fresh cut papaya can give you enough Vitamin C in just one cup. Every 100 g of papaya contains 60 mg of Vitamin C.
5. Tomatoes
Cooked or eaten raw in a salad, tomatoes are packed with multiple vitamins and provitamins. 100 g of raw cut tomatoes contain about 14 mg of Vitamin C.
6. Strawberry
This delicious berry is known to contain 58.8 mg of Vitamin C per 100 g serving.
In case you are unable to consume enough Vitamin C from dietary intake alone, supplementing Vitamin C with dietary supplement capsules or tablets could also be a good option.
In Conclusion…
Vitamin C is one of the most important nutrients that is involved in numerous bodily functions like immunity, collagen synthesis, protection from free radical damage, etc. Our body is unable to synthesize Vitamin C and must rely solely on dietary intake. Unfortunately, more than 45% of Indians are deficient in Vitamin C and are unable to fulfill the same with their regular diets. Proactively including Vitamin C rich foods in your daily diet or supplementing with Vitamin C dietary supplements is a wise decision to combat signs and symptoms of Vitamin C deficiency.
#ShareIfYouCare #RepublicOfDeficiency
Sources
[1] Ravindran RD, Vashist P, Gupta SK, Young IS, Maraini G, Camparini M, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for Vitamin C deficiency in North and South India: A two centre population based study in people aged 60 years and over. PLoS One 2011; 6 : e28588
[2] Immunity and India-India Fit Report 2019, GOQii,
[3] National Family Health Survey-4, 2015-16
[4] Emilie Brenaut, Laurent Misery, Charles Taieb, Sensitive Skin in the Indian Population: An Epidemiological Approach, Front Med (Lausanne). 2019; 6: 29.
[5] The persistence of memory: The burden of Alzheimer’s disease in India. Available at https://www.brookings.edu/blog/up-front/2019/09/20/the-persistence-of-memory-the-burden-of-alzheimers-disease-in-india/